Infectious disease
Anaplasmosis
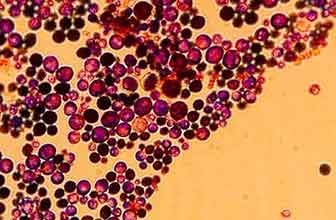
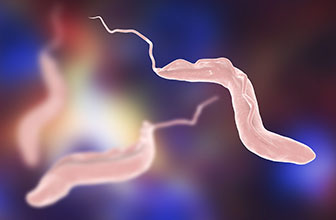
The anaplasmosis is a vector-borne disease caused by the bacterium Anaplasma phagocytophilum (previously called Ehrlichia phagocytophila), which attack the white blood cells of the blood. This emerging zoonoses affects both humans (human granulocytic anaplasmosis, HGA) and animals, mainly dogs, although it can also appear in cats, horses and sheep and cattle. Anaplasmosis is transmitted through tick bites, not through direct contact with infected animals. On rare occasions, it can be transmitted by blood transfusion. The symptoms are usually non-specific, such as apathy, fever, anorexia, an enlarged spleen, low levels of certain blood components, or lameness. The treatment consists of administering antibiotics, doxycycline, and the prognosis is usually favorable. As prevention it is recommended to avoid tick bites, checking the animal before and after each walk, avoiding wet areas and thickets, combing it and using antiparasitic products. The diagnosis is made by peripheral blood smear under a microscope, a serological test, or PCR.
Anaplasmosis is present worldwide, and is the most common tick-borne disease after borreliosis.
References of Anaplasmosis
RECOMBINANT ANTIGENS
Name, references, and description
Brochures
- Rekom Biotech catalogue
- Recombinant proteins for in vitro diagnosis of human infectious diseases
- Recombinant proteins for in vitro diagnosis of animal infectious diseases
- Farm animal infectious diseases
- Recombinant proteins for vector-borne diseases
- IVD reagents for Transfusion-Transmitted Infectious diseases
Videos
Specialists in IVD reagents for infectious disease diagnosis
We ensure a commitment to absolute confidentiality regarding all information received and generated related to your project.
-
[[carrito.product.name]]
- [[sku.sku]]
Or if you prefer...
We will analyze your request to prepare a quote tailored to your needs.
-
[[carrito.product.name]]
- [[sku.sku]]
As manufacturers, we can adapt our products to your needs.
Contact us!