Infectious disease
Chagas
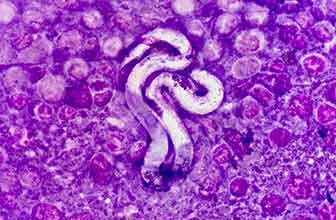
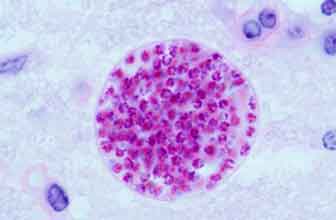
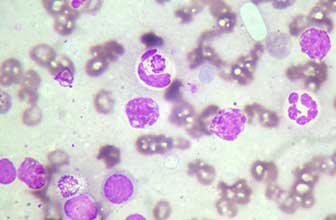
Chagas disease is a life-threatening zoonoses caused by the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi. It affects humans and animals, mainly dogs. Chagas transmission occurs through the bite of an infected insect, called a triatomine. After feeding, it defecates on the skin, and parasites found in its feces can enter the body through the eyes, mouth, wounds, or even the insect bite itself. It can also be transmitted through blood transfusion, organ transplant, ingestion of food contaminated with parasites, and from mother to child during pregnancy. The symptoms can range from mild to severe, and even no symptoms appear until the chronic stage. In the acute phase, the most common symptoms are fever, discomfort and inflammation of the area that has suffered the sting, and they usually subside without the need for treatment. Later, even over the years, and if it has not been treated, the disease can reactivate and enter the chronic phase, with more severe symptoms such as cardiac, digestive and neurological disorders. The treatment is carried out with antiparasitic drugs, and as prevention it is recommended to avoid endemic areas, the use of repellent and early diagnosis. The diagnosis of Chagas is one of the great challenges posed by this disease, given the importance of treating the infected person in the acute phase. But the diagnosis is also of vital importance to prevent infections through transfusions and organ transplants, to reduce vectorial transmission, for the detection and treatment of women of childbearing age, and as a screening of newborns and siblings of infected mothers without treatment. Diagnostic tests consist of serological tests and blood smears under a microscope.
Chagas disease is considered endemic in Latin America, but it has spread throughout the world: it is estimated that 6 to 7 million people worldwide are infected with Trypanosoma cruzi. It is a disease recognized by the WHO as one of the 13 most neglected tropical diseases in the world.
Dogs are risk factors for the transmission of Chagas: they have a high susceptibility to the parasite and a high probability of becoming infected at an early age. They are 14 times more effective at spreading the disease than humans, as they normally roost in areas easily accessible by infected insects. Also, when an animal is malnourished and its immune system is compromised, it has a higher risk of becoming infected.
References of Chagas
RECOMBINANT ANTIGENS
Name, references, and description
FRA
- RAG0005
- RAG0005BIOT (biotinylated)
- Cytoskeleton associated antigen. Also known as Ag1, JL7, H49
ChimChagas1
- RAG0093 (chimera)
- RAG0093BIOT (biotinylated,chimera)
- Multi-epitope recombinant chimeric antigen for Chagas
ChimChagas2
- RAG0094 (chimera)
- RAG0094BIOT (biotinylated, chimera)
- Multi-epitope recombinant chimeric antigen for Chagas
ChimChagas3
- RAG0096 (chimera)
- RAG0096BIOT (biotinylated, chimera)
- Multi-epitope recombinant chimeric antigen for Chagas
Brochures
- Rekom Biotech catalogue
- Recombinant proteins for in vitro diagnosis of human infectious diseases
- Recombinant proteins for in vitro diagnosis of animal infectious diseases
- IVD reagents for Neglected tropical diseases
- IVD reagents for Transfusion-Transmitted Infectious diseases
- IVD reagents for diagnosis of Chagas
Videos
Specialists in IVD reagents for infectious disease diagnosis
We ensure a commitment to absolute confidentiality regarding all information received and generated related to your project.
-
[[carrito.product.name]]
- [[sku.sku]]
Or if you prefer...
We will analyze your request to prepare a quote tailored to your needs.
-
[[carrito.product.name]]
- [[sku.sku]]
As manufacturers, we can adapt our products to your needs.
Contact us!